Using Klogging with SLF4J
The Simple Logging Façade for Java (SLF4J) library is a widely-used library for Java logging. It has two parts: a standard API that Java programs call; and a provider that maps API calls to a logging framework (e.g. Logback, Log4j).
Many Java programs and frameworks, including Spring, log using the SLF4J API.
Klogging has an SLF4J provider that allows existing programs using SLF4J to switch the framework to Klogging.
Klogging supports SLF4J versions 2.x as used by Spring Boot 3 and later.
Setting up
Include this dependency in your Gradle build file:
implementation("io.klogging:slf4j-klogging:0.11.7")
In Maven:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.klogging</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-klogging</artifactId>
<version>0.11.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Including values in messages
There are two options for including values in messages: SLF4J formatting with anchors or Klogging message templates.
SLF4J formatting with anchors
All existing logging statements with SLF4J formatting will continue to work with Klogging, for example:
logger.info("Captured value {}", captured);
In this example, the log event contains the message with {} replaced by the value of
captured and contains no items.
Message templates
With the Klogging provider, you can use message templates in SLF4J logging method calls and Klogging will emit structured log events. For example:
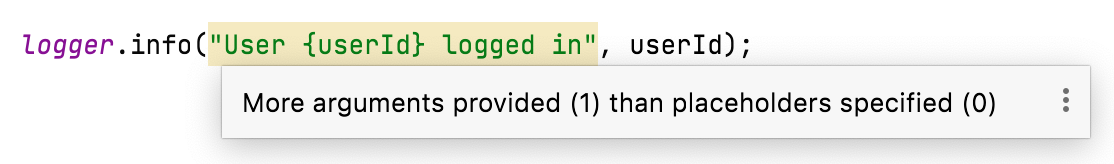
logger.info("User {userId} logged in", userId);
IntelliJ IDEA will highlight message templates in SLF4J logging method calls because
they are not the positional {} anchors used by SLF4J.
Using both SLF4J formatting and message templates in the same log statement might result in unexpected behaviour.
MDC
Klogging will include any information from the Mapped Diagnostic Context (MDC) in its log events. For example:
try (MDC.MDCCloseable closeable = MDC.putCloseable("runId", UUID.randomUUID().toString())) {
logger.info("Started processing");
processStuff();
logger.info("Finished processing");
}
All structured log events emitted in that block include the key runId
with the value for that run.
